Researchers have developed a high-performance microscopy system for non-invasive conjunctival goblet cells examination in patients, which was recognized for its technical advancement and potentials.
Conjunctival goblet cells (CGCs) are specialized epithelial cells secreting mucins to form the mucus layer of tear film. The mucus layer spreads the tear film on the ocular surface for protection.
The dysfunction and death of conjunctival goblet cells causes tear film instability and is associated with various ocular surface diseases including the dry eye disease (DED). Because dry eye disease is a multifactorial disease with multiple causes, it is important to find the causes and disease status. Therefore, CGC examination is important for the precise diagnosis and effective treatment of ocular surface diseases; however, conjunctival goblet cells microscopy examination has not been possible until now due to lack of non-invasive devices.
The new research was published in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, an international journal on medical imaging.
This study was led by a POSTECH research team spearheaded by Professor Ki Hean Kim and PhD candidates Jungbin Lee and Seonghan Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), in collaboration with professors Hong Kyun Kim and Byeong Jae Son (Department of Ophthalmology) of Kyungpook National University and Professor Chang Ho Yoon (Department of Ophthalmology) of Seoul National University, The new research was published in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, an international journal on medical imaging.
Earlier in 2019, the research team had discovered for the first time that moxifloxacin, an FDA-approved ophthalmic antibiotic, stains CGCs, and demonstrated high-contrast CGC imaging by using moxifloxacin as a cell labeling agent. However, conjunctival goblet cells imaging in humans was impossible due to various limitations of conventional microscopy techniques such as shallow depth-of-fields (DOFs) and slow imaging speeds.
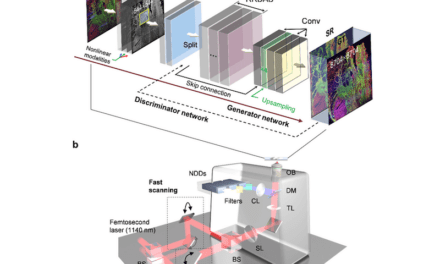
To overcome these limitations, the research team developed a high-speed extended DOF microscopy which had a 1 mm DOF (25x DOF extension) and 10 frames per second imaging speed. A deformable mirror was used in the system to axially sweep the imaging plane and to capture CGCs on the arbitrary tilted conjunctiva in single frames. The acquired images contained both in-focus and out-of-focus information, and the deconvolution was used to filter the in-focus information only. A system schematic and example images are shown in the above image.
“The newly developed imaging system can obtain high-resolution in-focus images of CGCs in live animal models and is also applicable to humans,” says Professor Ki Hean Kim of POSTECH. “Going forward, we will develop a device for imaging patients and then run clinical trials to test the feasibility of non-invasive CGC examination in the diagnosis and treatment of ocular surface diseases.”
This study was conducted with the support from the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center (Project number SRFC-IT2101-05)
Featured image: Image acquisition and image processing using the mouse conjunctiva as an example. Photo: POSTECH