Summary:
A new study highlights the role of tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for digestive tract diseases, offering insights into their regulatory functions and clinical applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Biological Role – these RNAs influence crucial cellular processes like translation regulation, epigenetic modification, and protein interactions.
- Diagnostic & Therapeutic Potential – tsRNA expression profiles correlate with gastrointestinal diseases, making them promising biomarkers and drug targets.
- Clinical Applications – Advances in sequencing and targeted therapies suggest tsRNAs could revolutionize precision medicine and improve disease management.
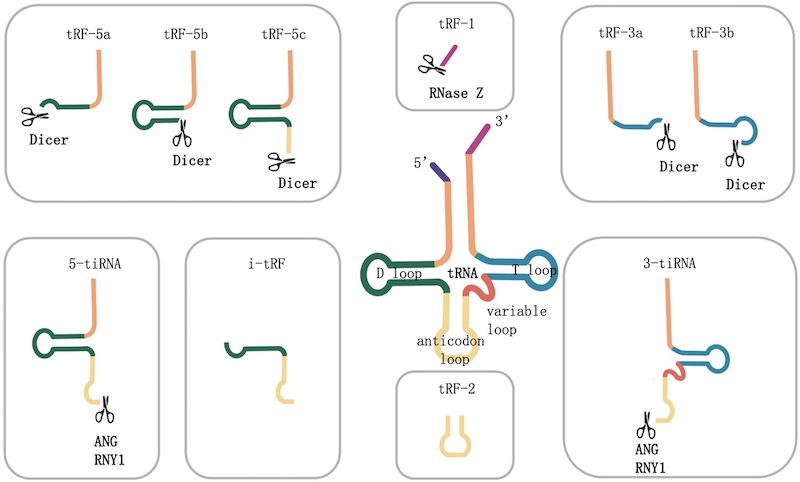
A new article published in Genes & Diseases highlights the critical role of tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) in digestive tract diseases, positioning these molecules as potential biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and targeted therapies. The comprehensive review explores the biogenesis, classification, and biological functions of tsRNAs, shedding light on their influence over cellular processes such as translation regulation, epigenetic modification, and protein interactions.
tsRNAs May ID Various Gastrointestinal Diseases and Cancers
Recent findings emphasize the significance of tsRNAs in both tumor and non-tumor digestive diseases, demonstrating their ability to regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and immune responses. The molecular mechanisms behind these functions suggest a close association between expression profiles and various gastrointestinal conditions, including gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver disease, biliary tract disorders, and pancreatic disease. By modulating crucial signaling pathways, tsRNAs could serve as early diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets, transforming current approaches to digestive health.
One of the most compelling aspects of the research is the potential application of for interventions. By leveraging tsRNA-targeted drugs, scientists have successfully altered disease phenotypes in preclinical models, paving the way for new therapeutic strategies. These findings hold promise for the development of personalized medicine, where tsRNA expression levels could guide treatment decisions and patient monitoring.
Predictive Capabilities
The widespread presence and high conservation of these RNA types in digestive tract diseases underscore their clinical value. Researchers have identified specific tsRNA molecules with predictive capabilities, enabling more precise disease monitoring. Advances in sequencing technology have further enhanced the ability to detect tsRNA expression patterns, improving diagnostic accuracy and offering novel insights into disease mechanisms.
The implications of these discoveries extend beyond the realm of diagnostics. As tsRNA-targeted therapies continue to evolve, their integration into clinical practice could revolutionize the management of digestive diseases. The potential for combining tsRNA-based treatments with existing therapies presents exciting new avenues for improving patient outcomes and enhancing precision medicine approaches.
This emerging field holds transformative potential, promising to refine disease detection, improve therapeutic efficacy, and expand our understanding of RNA-based regulation in digestive tract disorders. With continued research and technological advancements, tsRNAs may soon become a cornerstone in the fight against digestive tract diseases.
Featured Image: Biogenesis and classification of tsRNAs. tsRNA is divided into two types: tRFs and tiRNAs. Image: Genes & Diseases