Researchers from the University of Notre Dame and the University of Florida have developed a sensor that could diagnose a heart attack in less than 30 minutes, according to a study published in Lab on a Chip.
Initial results from an echocardiogram can quickly show indications of heart disease, but to confirm a patient is having a heart attack, a blood sample and analysis is required. Those results can take up to eight hours.
“The current methods used to diagnose a heart attack are not only time-intensive, but they also have to be applied within a certain window of time to get accurate results,” says Pinar Zorlutuna, PhD, a Sheehan Family Collegiate Professor of Engineering at Notre Dame and lead author of the paper. “Because our sensor targets a combination of miRNA, it can quickly diagnose more than just heart attacks without the timeline limitation.”
By targeting three distinct types of microRNA or miRNA, the newly developed sensor can distinguish between an acute heart attack and a reperfusion.
“The technology developed for this sensor showcases the advantage of using miRNA compared to protein-based biomarkers, the traditional diagnostic target,” says Hsueh-Chia Chang, PhD, a Bayer Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at Notre Dame and co-author of the paper. “Additionally, the portability and cost efficiency of this device demonstrates the potential for it to improve how heart attacks and related issues are diagnosed in clinical settings and in developing countries.”
A patent application has been filed for the sensor and the researchers are working with Notre Dame’s IDEA Center to potentially establish a startup company that would manufacture the device.
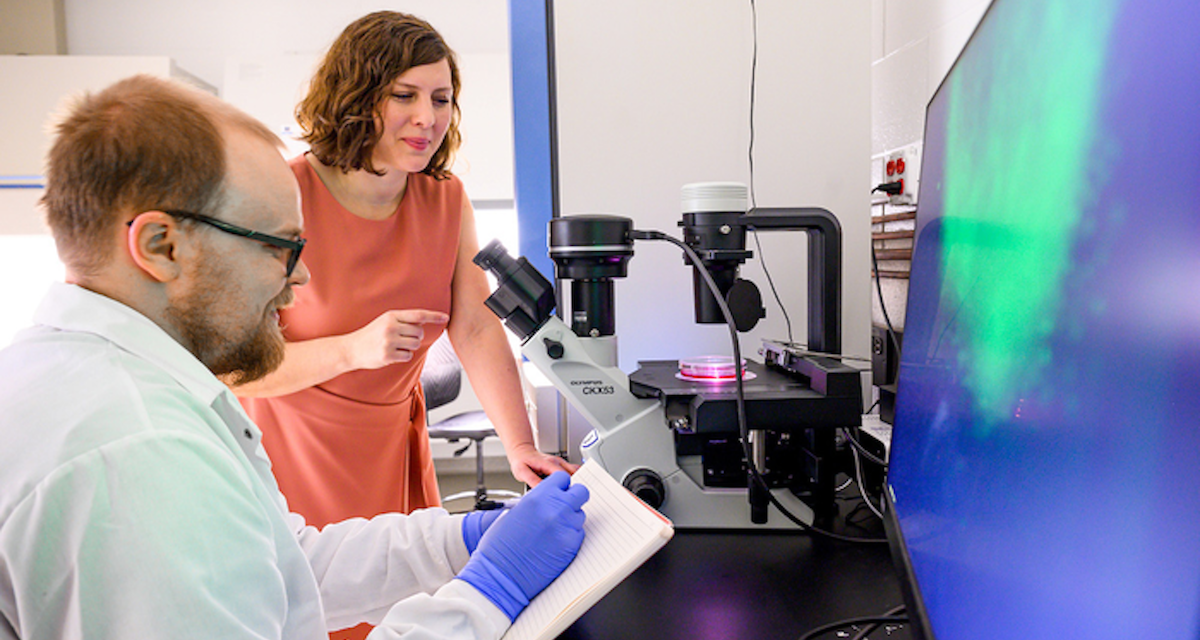
Featured image: Pinar Zorlutuna talks with one of her graduate students in her lab. Photo: Matt Cashore/University of Notre Dame