Summary
In the evolving landscape of clinical diagnostics, pre-analytical errors continue to challenge laboratory technicians. Key issues, such as mislabeling or improper specimen handling, affect result accuracy. By understanding these errors and implementing preventative strategies, laboratories can enhance efficiency and test results reliability—a critical aspect given increasing testing volumes.
Key Takeaways
- Pre-analytical errors are a significant part of the total errors in laboratory diagnostics and must be rigorously managed.
- Common errors include specimen mislabeling and incorrect handling, both of which can compromise test accuracy.
- Implementing clear protocols and harnessing new technology can greatly reduce the occurrence of these errors.
- Continuous staff training and regulatory updates are crucial in maintaining best practices.
In the sphere of clinical laboratories, pre-analytical errors represent a substantial proportion of the total error count. These errors occur before the actual analysis of the specimen and can greatly influence the reliability of test results. A typical example is mislabeling, which can lead to severe consequences such as incorrect patient treatment. In fact, studies have shown that mislabeling contributes to a significant portion of diagnostic inaccuracies.
Moreover, improper specimen handling—including incorrect storage temperature and timing before analysis—impacts the integrity of samples. As testing demands rise and timelines tighten, the potential for these errors also escalates. Other errors such as incorrect patient identification and improper sample collection techniques further compromise the diagnostic process.
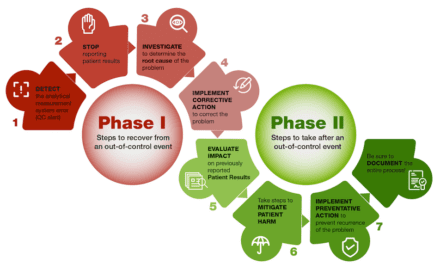
Given the high-pressure environment and ever-increasing volume of tests, laboratories must be diligent in minimizing these pre-analytical errors. The adoption of advanced technologies and strict compliance with regulatory standards can play a role in achieving this goal.
Strategies to Mitigate Pre-Analytical Errors
To reduce pre-analytical errors, laboratories can implement comprehensive strategic approaches focusing on technology, personnel, and processes. Developing stringent protocols and using barcoding systems for specimen labeling, for instance, can minimize mislabeling errors. Barcoding not only improves accuracy but also synchronizes data management across multiple platforms, reducing human errors.
Proper personnel training is another key component. Continuous education on best practices and regular training sessions can ensure that staff members are updated on the latest techniques and regulatory requirements. Incorporating scenario-based learning methods further strengthens the practical understanding of error prevention.
Ensuring the specimens are handled correctly from collection to analysis remains fundamental. Employing digital temperature monitors and alarm systems for storage areas can prevent issues stemming from improper temperatures. Adopting sample track systems that monitor the specimen journey can help identify potential mishandling early.
On the regulatory front, staying abreast of updates from governing bodies such as CLIA and CAP is essential. New guidelines can affect laboratory processes and shape the implementation of preventive measures. Moreover, engaging in audits and external quality assessments can provide insights into gaps and offer scope for improvements.
As testing volumes continue to soar, embracing new methodologies and technological assistance becomes indispensable for reducing pre-analytical errors. These strategies help maintain accuracy and efficiency, which are paramount for the effective functioning of clinical diagnostics laboratories.