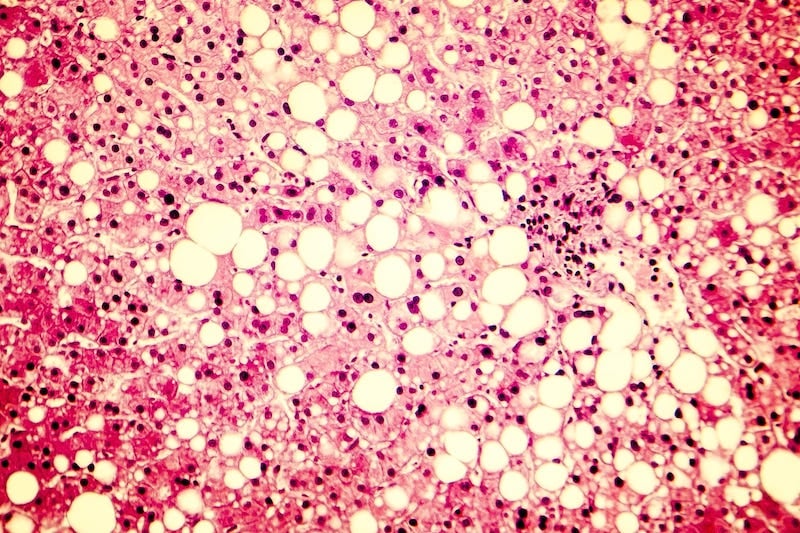
Summary: Luxor Scientific and CIMA Sciences have launched OWLiver, a non-invasive blood test to detect all stages of metabolic liver disease, aligning with the FDA’s recent approval of a new MASH treatment.
Takeaways:
- OWLiver offers a non-invasive alternative to liver biopsies for detecting MASLD and MASH.
- The test utilizes the MASEF score and advanced metabolomics technology to identify at-risk individuals early.
- MASLD, affecting over 30% of U.S. adults, is linked to rising obesity and diabetes rates, highlighting the importance of early detection and new treatments.
Luxor Scientific and CIMA Sciences join forces for the US launch of OWLiver, an exclusive non-invasive blood test able to detect all dangerous stages of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). The OWLiver metabolic assay meets the urgent need for a non-invasive test for identification of individuals who have “at-risk” MASH and are at high risk for progressing to end-stage liver disease. This collaboration coincides with the FDA’s March 2024 approval of the first and only medication for MASH treatment, marking a transformative step forward in enhancing liver disease testing and management, according to the companies.
Further Reading: Diagnosing and Managing Steatotic Liver Disease
Luxor Scientific is the only laboratory offering CIMA Sciences’ OWLiver testing in the US, which utilizes the MASEF (metabolomics-advanced steatohepatitis fibrosis) score.1 With advanced metabolomics technology, this test holds the potential to transform approaches in understanding and treating metabolic dysfunction associated liver conditions.
“As we continue to see a rise in metabolic syndrome in the US, MASLD is becoming more and more prominent,” says Marion Snyder, PhD, DABCC, of Luxor Scientific. “For years, physicians have had to rely on invasive liver biopsy procedures and costly imaging studies. OWLiver can identify MASLD in its early stages, giving patients the chance to stop and reverse the disease and live a healthier lifestyle.”
MASLD, previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is the most common cause of chronic liver disease, impacting over 30% of adults in the US, and is expected to increase in the coming years with the steady rise of obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. As many as 20% of type 2 diabetic individuals with MASLD will develop MASH. Studies show that 15-20% of patients with MASH can progress to liver disease and ultimately liver failure. Early identification of “at-risk” MASH is a priority, as these patients are at increased risk for disease progression and may benefit from developed therapies to prevent the disease and further liver damage and related complications.
“The availability of this test is incredibly significant for patients at this time,” says Alejo Llopart-Mascaro of CIMA Sciences. “We take pride in our collaboration with Luxor Scientific to address the growing issue of metabolic associated liver disease. This partnership enables healthcare providers to diagnose and subsequently offer effective treatments that are now readily available to their patients.”
REFERENCE
[1] The Metabolomics-Advanced steatohepatitis fibrosis score (MASEF). Hepatology. 2024 Jan 1;79(1):135-148.doi: 10.109724